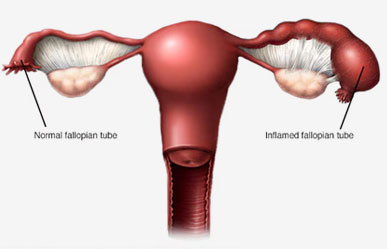
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs—including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It’s a serious condition that requires prompt treatment by a gynaecologist to prevent long-term complications like infertility, chronic pelvic pain, or ectopic pregnancy.
What Causes PID?
PID usually results from a bacterial infection that spreads from the vagina or cervix upward into the uterus and fallopian tubes. Common causes include:
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea
- After childbirth, miscarriage, abortion, or IUD insertion
- Poor vaginal hygiene or untreated vaginal infections
Common Symptoms of PID:
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Fever and chills
- Abnormal vaginal discharge (foul-smelling, yellow/greenish)
- Pain during sex
- Burning during urination
- Irregular menstrual bleeding
Some women may have mild or no symptoms, especially in early stages—making regular gynaecological check-ups important.
How a Gynaecologist Diagnoses PID:
- Pelvic exam
- Vaginal swabs and cervical cultures (to check for infection)
- Blood tests
- Ultrasound (to check for abscesses or inflamed tubes)
- In some cases, laparoscopy may be done for confirmation
Treatment of PID:
- Antibiotics (oral or injectable) – started immediately
- Hospitalization if:
Severe symptoms
Pregnant
Abscess present
- Partner treatment – to avoid reinfection
- Surgical drainage – in rare cases if abscesses form or don’t respond to medication
Complications if Untreated:
- Infertility
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Ectopic pregnancy (life-threatening)
- Tubo-ovarian abscess
Preventing PID:
- Practice safe sex (use condoms)
- Get regular STI screenings
- Prompt treatment of any vaginal infections
- Avoid frequent vaginal douching (it disturbs natural flora)