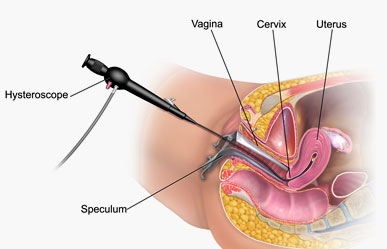
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows a gynaecologist to look inside the uterus using a thin, lighted tube called a hysteroscope. It is used for both diagnosis and treatment of various uterine problems.
Why is Hysteroscopy Done?
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy helps investigate:
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Repeated miscarriages
- Infertility
- Abnormal ultrasound findings (polyps, fibroids, etc.)
Operative Hysteroscopy is used to treat:
- Uterine polyps or fibroids
- Adhesions (Asherman’s syndrome)
- Septate uterus
- Retained products of conception
- Removal of IUD
- Endometrial ablation (for heavy bleeding)
How is it Performed?
- Usually done in an outpatient setting or operation theatre
- No incisions—hysteroscope is inserted through the vagina and cervix
- Can be done under local, regional, or general anesthesia
- Saline or gas is used to expand the uterus for better visibility
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive (no cuts)
- Quick recovery (often same-day discharge)
- Accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment
- Preserves uterus and fertility in many cases