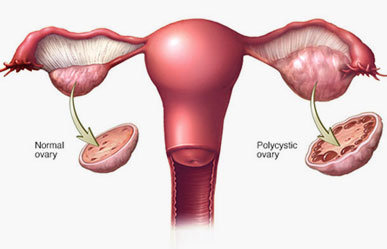
PCOD
PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease), also called PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome), is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is one of the most frequent reasons why women visit a gynaecologist, especially for issues related to periods, weight gain, skin problems, or difficulty getting pregnant.
What Happens in PCOD?
- The ovaries produce multiple small cysts (fluid-filled sacs)
- There is a hormonal imbalance – especially increased androgens (male hormones)
- This leads to irregular periods, delayed ovulation, and other symptoms
Common Symptoms of PCOD:
- Irregular or missed periods
- Excess facial/body hair (hirsutism)
- Acne and oily skin
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Hair thinning or scalp hair loss
- Difficulty conceiving (infertility)
- Mood swings or depression
Causes:
Exact cause is unclear, but risk factors include:
- Genetics (family history)
- Insulin resistance
- Unhealthy lifestyle (poor diet, lack of exercise)
How a Gynaecologist Helps:
1. Diagnosis – Through:
- Menstrual history
- Hormone blood tests
- Pelvic ultrasound (to check for cysts)
2. Treatment Options:
- Lifestyle changes: Healthy diet, regular exercise, weight loss
- Medications:
Hormonal pills (to regulate periods)
Metformin (for insulin resistance)
Fertility medicines (if trying to conceive)
- Cosmetic treatments: For acne or excess hair
3. Fertility Support:
- Ovulation-inducing medications
- Advanced options like IUI/IVF if needed
Long-Term Risks of Untreated PCOD:
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Endometrial (uterine) cancer
- Depression/anxiety