Family Planning Surgery
Family planning surgery, also known as female sterilization, is a permanent method of contraception for women who do not wish to have more children. It involves blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes so that the egg cannot meet the sperm, thereby preventing pregnancy.
Types of Family Planning Surgery
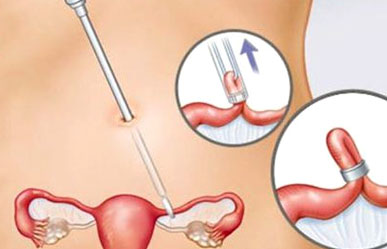
1. Tubal Ligation (Tubectomy):
- Most common method
- Fallopian tubes are cut, tied, or sealed
- Can be done through:
Minilaparotomy (Mini-lap) – small abdominal incision
Laparoscopic sterilization – using a camera and instruments through small keyhole incisions
2. Postpartum Sterilization:
- Done immediately after delivery (within 48 hours), especially after a C-section
Benefits:
- Permanent and highly effective
- No need for daily pills or regular contraception
- No effect on hormones or menstrual cycle
- Done as a daycare procedure (especially laparoscopy)
- Quick recovery (usually within 2–3 days)
Ideal Candidates:
- Women who are sure they do not want future pregnancies
- Usually over the age of 25, with 2 or more children (as per public health guidelines)
- Should be mentally and emotionally ready for permanent contraception
Counseling is Important:
- Gynaecologists provide detailed counseling to ensure the woman is fully informed
- The decision should be voluntary, without pressure
- Reversible methods like IUDs or implants may be discussed as alternatives