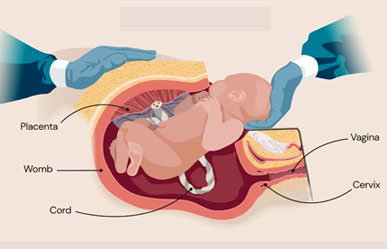
Caesarean Section
A Caesarean Section (commonly called a C-section) is a surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through an incision in the mother’s abdomen and uterus. It is performed by a gynaecologist/obstetrician, either as a planned (elective) or emergency procedure.
When is a C-section Done?
Planned (Elective):
- Baby is in breech (feet or buttocks first)
- Multiple pregnancies (twins/triplets)
- Placenta previa (placenta covering cervix)
- Previous C-section (depending on case)
- Maternal health issues (like high BP, diabetes)
Emergency:
- Labor isn’t progressing
- Fetal distress (baby’s heartbeat is abnormal)
- Cord prolapse (umbilical cord comes out before baby)
- Uterine rupture
How is the Procedure Done?
- Spinal or epidural anesthesia is usually given (mother is awake but numb from the waist down).
- A horizontal incision is made just above the pubic area.
- The baby is delivered through the uterus.
- Placenta is removed, and the incision is closed with sutures.
Recovery After C-section
- Hospital stay: 3–5 days
- Full recovery: 6–8 weeks
- Pain and movement restrictions initially
- Special care for surgical wound