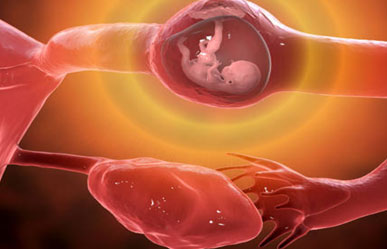
Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. It cannot continue as a normal pregnancy and requires prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Where Can an Ectopic Pregnancy Occur?
- Fallopian tubes (most common – tubal pregnancy)
- Ovary
- Cervix
- Abdominal cavity
- Cesarean scar (rare)
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy:
- Sharp or stabbing lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Vaginal spotting or bleeding
- Shoulder pain (from internal bleeding)
- Dizziness or fainting (sign of rupture)
- Missed period with positive pregnancy test
Risk Factors:
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Surgery on fallopian tubes
- Use of intrauterine device (IUD)
- Smoking
- Fertility treatments (e.g., IVF)
Diagnosis:
- Transvaginal ultrasound (to check if pregnancy is in the uterus)
- Blood tests (beta-hCG levels not rising as expected)
Recovery and Follow-Up:
- Regular monitoring of beta-hCG levels until they return to zero
- Rest and avoid strenuous activities
- Psychological support may be needed due to emotional impact
Future Fertility:
- Many women can conceive naturally after an ectopic pregnancy
- Close monitoring in future pregnancies is crucial to rule out recurrence
- IVF may be an option if both tubes are damaged/removed